
Participation in Crowdfunding Can Generate up to 73% in Returns Annually
Backers of projects on crowdfunding platforms can expect rewards from their pledges. For example, funding someone's idea on Kickstarter can result in an average annual return of 11.5%, with design projects known to deliver returns as high as 70%. However, it is important to note that these returns do not come in the form of direct cash payments but rather as savings on the purchase of the product once it hits the market. This has been demonstrated in a study by researchers at the HSE Faculty of Economics published in Economic Analysis Letters.

Scientists Rank Foreign Languages by Their Benefit for the Brain
An international team of researchers, with the participation of scientists from the HSE Institute for Cognitive Neuroscience, studied how the choice of a foreign language affects human cognitive abilities. It turns out that languages greatly differing from one's native language stimulate cognitive function at the initial stage of their study, while those similar to the native language have a delayed effect and help the brain work more efficiently at a higher level of proficiency in a foreign language. The results of the study have been published in the journal Bilingualism: Language and Cognition.

Processing Temporal Information Requires Brain Activation
HSE scientists used magnetoencephalography and magnetic resonance imaging to study how people store and process temporal and spatial information in their working memory. The experiment has demonstrated that dealing with temporal information is more challenging for the brain than handling spatial information. The brain expends more resources when processing temporal data and needs to employ additional coding using 'spatial' cues. The paper has been published in the Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience.

Communication Can Increase Public Concern about Climate Change
An international team of researchers including scientists at HSE University have tested 11 communication strategies aimed to encourage pro-environmental behaviours. The sample included nearly 60,000 individuals from 63 countries. While interventions aimed at reducing psychological distance from climate problems proved to be effective, those targeting behaviours which require more effort, such as tree-planting or reducing one's carbon emissions, were not as successful. The study findings have been published in Scientific Advances.

Psychologists Study Daydreaming in Russian Cultural Context
Researchers at HSE University, having examined the role of daydreaming in the Russian cultural context, conclude that constructive daydreaming can help people with gaining insight into their life's trajectory, fostering personal growth, discovering existential meaning, enhancing psychological wellbeing, and cultivating a balanced temporal perspective. The study findings have been published in Cultural-Historical Psychology.
Neuroscientists Inflict 'Damage' on Computational Model of Human Brain
An international team of researchers, including neuroscientists at HSE University, has developed a computational model for simulating semantic dementia, a severe neurodegenerative condition that progressively deprives patients of their ability to comprehend the meaning of words. The neural network model represents processes occurring in the brain regions critical for language function. The results indicate that initially, the patient's brain forgets the meanings of object-related words, followed by action-related words. Additionally, the degradation of white matter tends to produce more severe language impairments than the decay of grey matter. The study findings have been published in Scientific Reports.
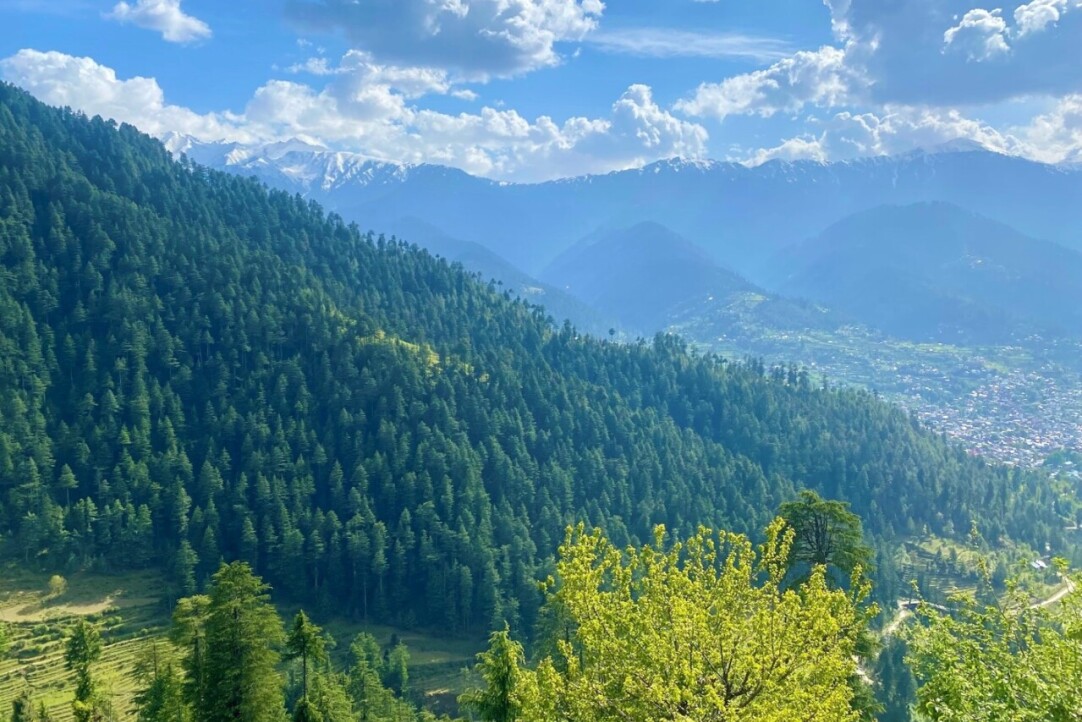

'Joint Background in Political Science and Anthropology Turned Out to Be Invaluably Useful in Studying the Region'
From April 26 to May 7, a team of professors and students from HSE University-St Petersburg conducted a field study in the Indian Himalayas. Below, Aleksei Sorbale, academic supervisor of the Bachelor's programme 'Political Science and World Politics', and Pavel Bazarov, a student of the Master's programme 'Global and Regional History', speak about their research and share their impressions of the expedition.
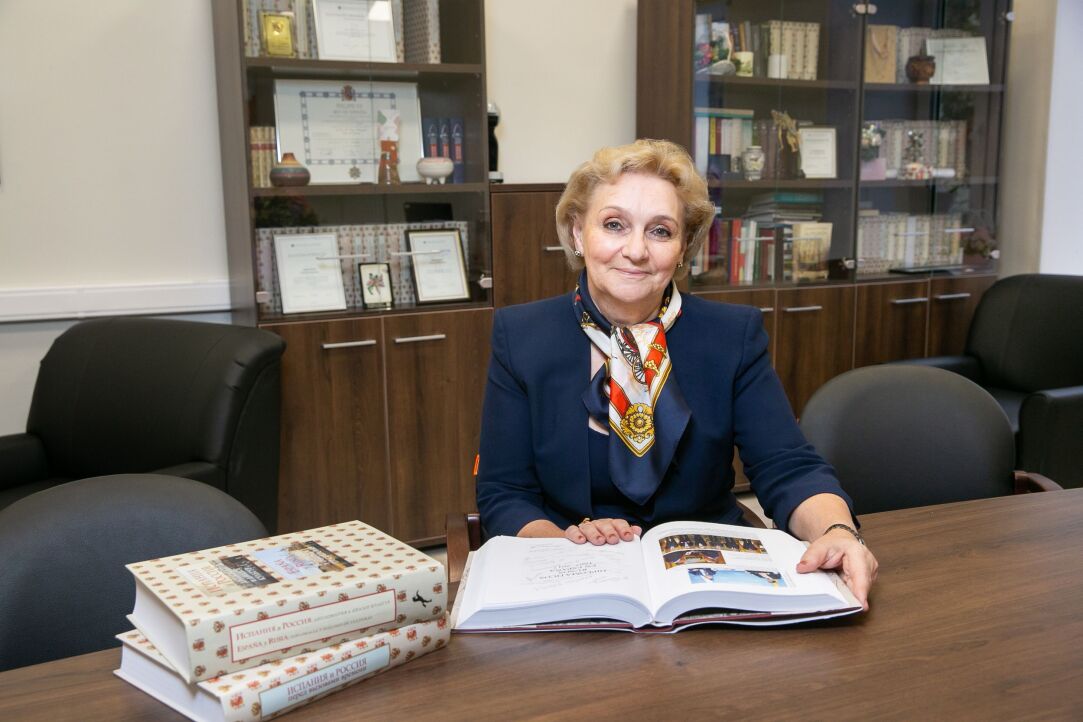

‘Compare Viewpoints, Listen to Others, and Try to Make Yourself Heard’
Prof. Olga Volosyuk, Head of the School of International Regional Studies, Faculty of World Economy and International Affairs, spoke to the HSE News Service about international relations, research, and conferences organised by the School.

Scientists Propose Star-Shaped Diffusion Model
Scientists at the AI Research Centre and the Faculty of Computer Science at HSE University, the Artificial Intelligence Research Institute (AIRI), and Sber AI have come up with novel architecture for diffusion neural networks, making it possible to configure eight distinct types of noise distribution. Instead of the classical Markov chain model with Gaussian distribution, the scientists propose a star-shaped model where the distribution type can be selected and preset. This can aid in solving problems across various geometric modalities. The results were presented at the NeurIPS 2023 conference.

HSE Scientists Leverage AI to Accelerate Advancement of 5G and 6G Wireless Communication Systems
The HSE Artificial Intelligence Centre has developed software for modelling radio channels in 5G and 6G wireless networks, based on ray tracing and machine learning techniques. Their software solutions enable modelling radio wave propagation between transmitters and receivers and can convert ray tracing data into a frame sequence format, configure and train neural networks based on this data, and subsequently save the trained models.

