HSE University’s CubeSX-HSE Satellite Launched into Orbit
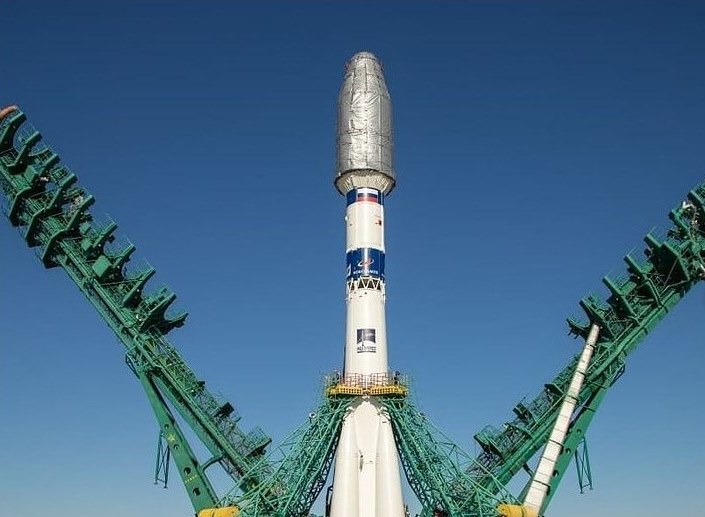

On March 22 at 9:07 Moscow time, a Soyuz-2.1a rocket with a Fregat upper stage was successfully launched. The launch vehicle carried a total of 38 satellites from 18 countries into sun-synchronous orbits, including HSE University’s CubeSX-HSE satellite, which will conduct remote sensing of the Earth.
HSE University’s satellite was developed jointly by experts from the Laboratory of Space Vehicles and Systems’ Functional Safety of the HSE Tikhonov Moscow Institute of Electronics and Mathematics (MIEM HSE) and Sputnix, a privately-owned space company.
CubeSX-HSE is a small spacecraft comprised of three blocks (each block being approximately 10 cm x 10 cm) mounted on a single frame. One of the units holds a flywheel assembly that orients the vehicle in space, the second includes all the boards for satellite operation, and the third is entirely dedicated to the payload — a camera for remote sensing of the Earth.
The vehicle is based on the OrbiCraft-Pro 3U CubeSat platform, one of the company’s products, and it is equipped with an experimental Fresnel lens camera developed at Samara University with a high-speed X-band transmitter. The satellite's control systems were developed by MIEM HSE staff and students.

The same flight delivered another satellite into orbit — a joint development of MIEM HSE, Sputnix, and the Sirius Educational Centre as part of the Grand Challenges programme for schoolchildren, where MIEM HSE specialists served as teachers and project managers. The two vehicles were built simultaneously and are largely identical; even their names are similar: CubeSX-HSE and CubeSX-Sirius-HSE. All telemetry reception from the Educational Centre satellite will be handled by the MIEM HSE Mission Control Centre, which is deployed and operated at MIEM HSE.
CubeSX-HSE will begin transmitting information to the Mission Control Centre as soon as possible.

Dmitrii Abrameshin, Lead Engineer, Laboratory of Space Vehicles and Systems’ Functional Safety
We are now preparing to fly satellites over our hardware and software complex. This will take place at about 10:00 pm and then again at midnight. At that time, our specialists will communicate with the satellites and receive telemetry information from them. First of all, they will check the satellite’s condition as well as the functioning of all systems and payloads. In the future, we are already planning to receive images from the remote sensing camera.
By controlling the satellite and receiving and processing information, the students will be able to solve practical, everyday tasks associated with the cubesats in orbit. Ensuring the reception of telemetry information at low altitudes, calculating the necessary frequency shift to compensate for the Doppler effect, and automatically adjusting the frequency during reception and transmission to account for this shift are just some of the tasks. In all of these tasks, students will not only gain deeper expertise in their areas of specialization, but will also acquire unique engineering experience working with small spacecraft.
To receive information from the satellite, a transmitting and receiving VHF radio station, Zavitok-M, developed at Sputnix, has been installed on the roof of a MIEM HSE building. The complex ensures the reception of telemetry from small spacecraft in low earth orbit and the transmission of control commands to them in accordance with amateur radio communication regulations. To date, the necessary antenna commissioning work has been carried out and telemetry reception tests from NOAA satellites (Polar-orbiting meteorological satellites designed for Earth observation) have been performed.

Data processing is a separate and important part of the work that will take place in close cooperation with Skanex. It is the only company in Russia that directly receives and processes remote sensing data to its own network of stations using unique technologies through geoportal services.
The laboratory team and the administration of MIEM HSE would like to thank the Foundation for Assistance to Small Innovative Enterprises in Science and Technology and Professor Ivan Bortnik for facilitating the project and supporting it at all stages.
The launch is operated by the commercial company, GK Launch Services. A total of 38 satellites from 18 countries were launched into orbit. Originally scheduled for March 20, the launch was postponed to March 22 for technical reasons.
See also:
Second HSE University Satellite Launched from Baikonur
On August 9, a Soyuz 2.1b rocket launched with a payload of HSE University’s second satellite, which will monitor the land surface of the Arctic region. HSE MIEM Deputy Director Andrey Abrameshin spoke about the university’s space plans, while Top Class competition winner Alexey Gilenko shared his impressions of the launch at Baikonur Cosmodrome.
HSE University Is Preparing to Launch its Second Satellite into Space
Only one year ago, the first HSE University satellite, developed by specialists and students from the Laboratory of Space Vehicles and Systems’ Functional Safety of the HSE Tikhonov Moscow Institute of Electronics and Mathematics (MIEM HSE) and the Sputnix space company, was launched into orbit. And now, the date of the second HSE University’s satellite launch has been announced: Roscosmos will send it into space from Baikonur Cosmodrome on August 9th, 2022.
240 Million Kilometres: HSE Satellite Spends a Year in Orbit
A year ago, on March 22, 2021, at 9:07 Moscow time, a Soyuz-2.1a rocket with a Fregat upper stage was successfully launched from Baikonur Cosmodrome Site 31. The launch vehicle carried 38 satellites, including the CubeSX-HSE satellite developed through the joint efforts of experts and students from the HSE University Laboratory of Space Vehicles and Systems’ Functional Safety of the HSE Tikhonov Moscow Institute of Electronics and Mathematics (HSE MIEM) and Sputnix, a privately-owned space company.
HSE University Participates in Satellite Navigation Monitoring Project
A team of HSE students is taking part in the development of a Russian satellite automatic identification system (AIS) to monitor sea navigation. The aim of the project is to track the locations of vessels and adjust their routes, including in the Arctic along the Northern Sea Route.
‘The Trip to Baikonur Blew My Mind!’
On Cosmonautics Day, the HSE News Service spoke with the participants of the CubSX-HSE project, which recently launched a satellite into Earth orbit. Students and staff from the HSE Moscow Institute of Electronics and Mathematics (MIEM) spoke about their project and impressions of their trip to Baikonur.
HSE to Open New Mission Control Centre
The Moscow Institute of Electronics and Mathematics (MIEM) has signed an agreement with Sputnix, a company that produces components for high-tech satellites. The agreement envisions, among other things, the creation of a mission control centre for small scientific and educational microsatellites. The centre will be part of MIEM.